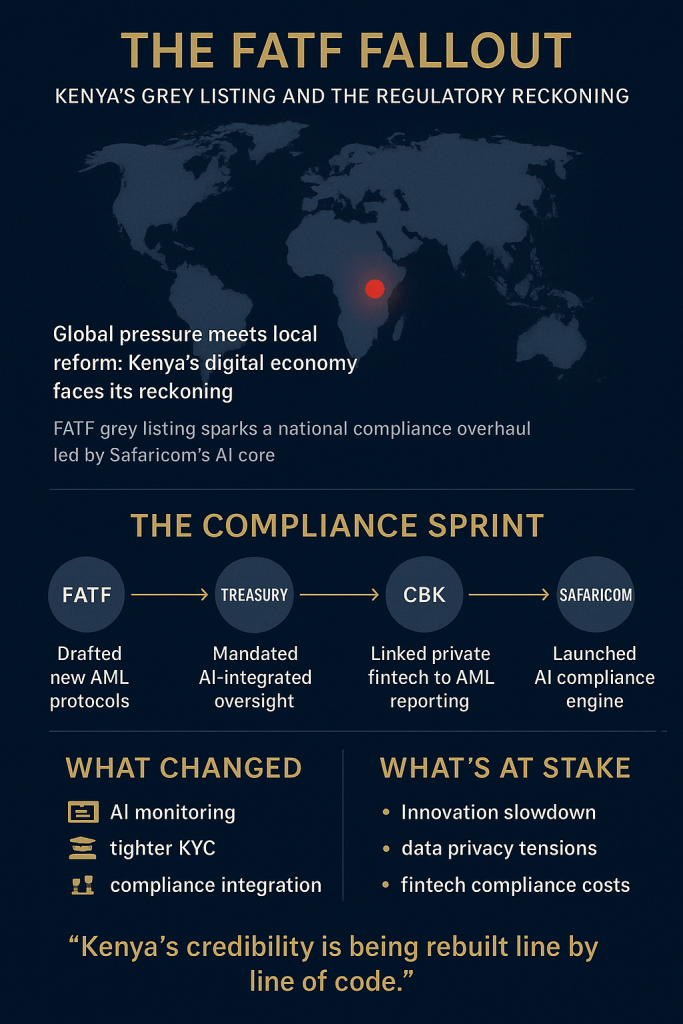
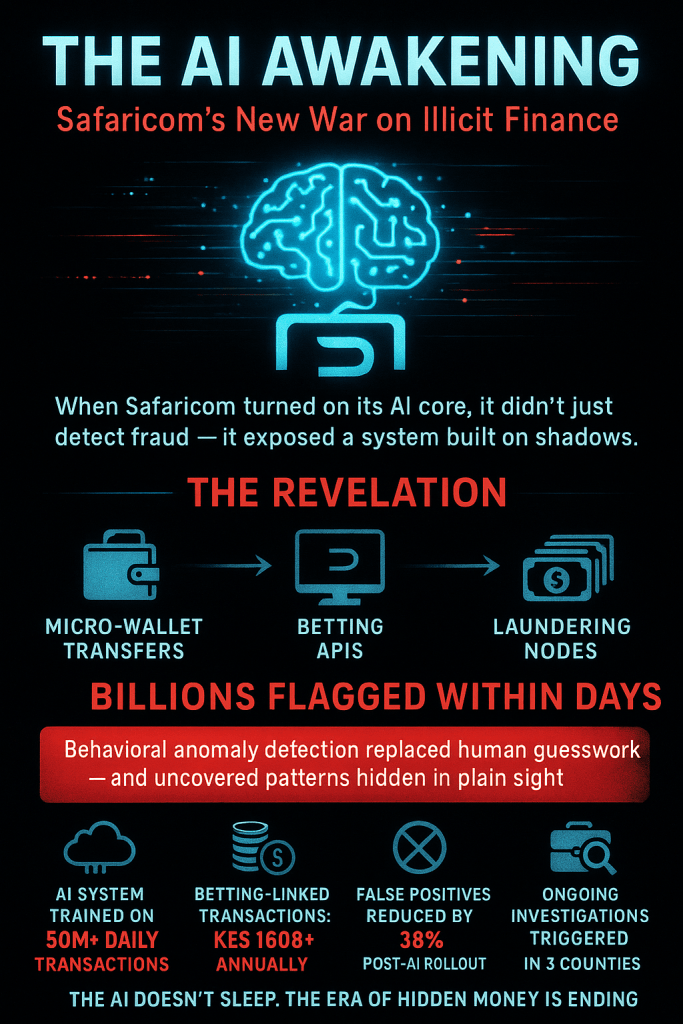
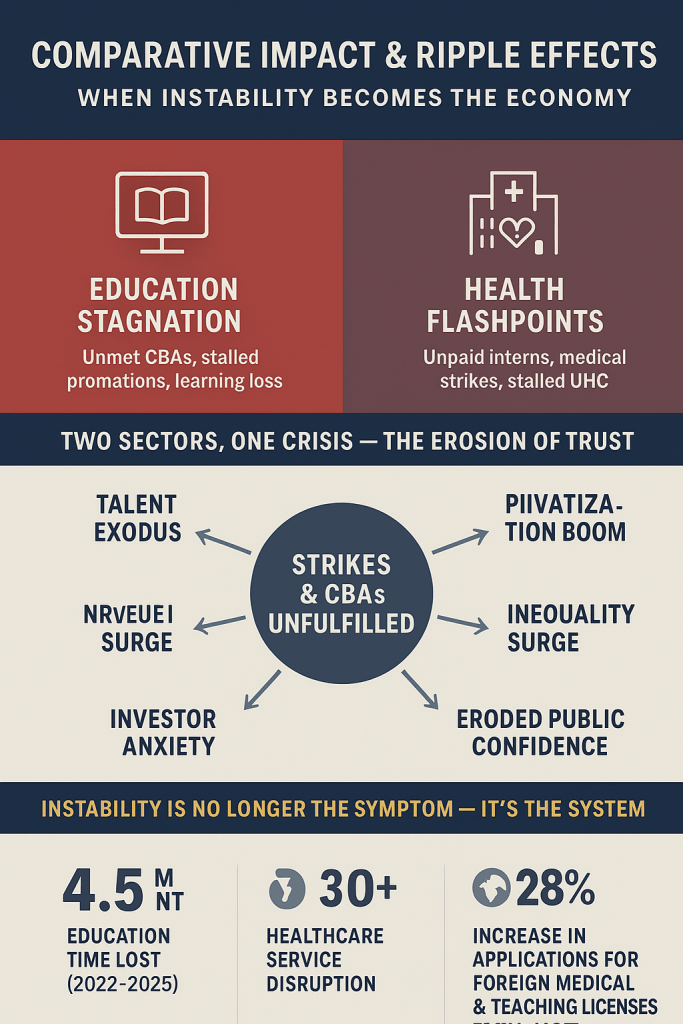
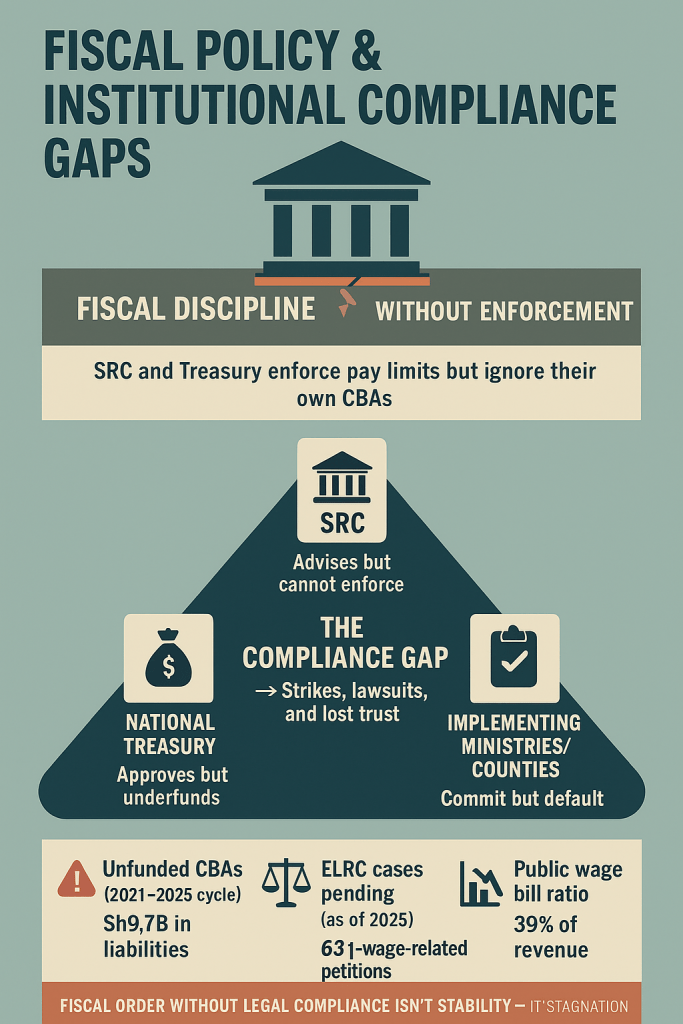
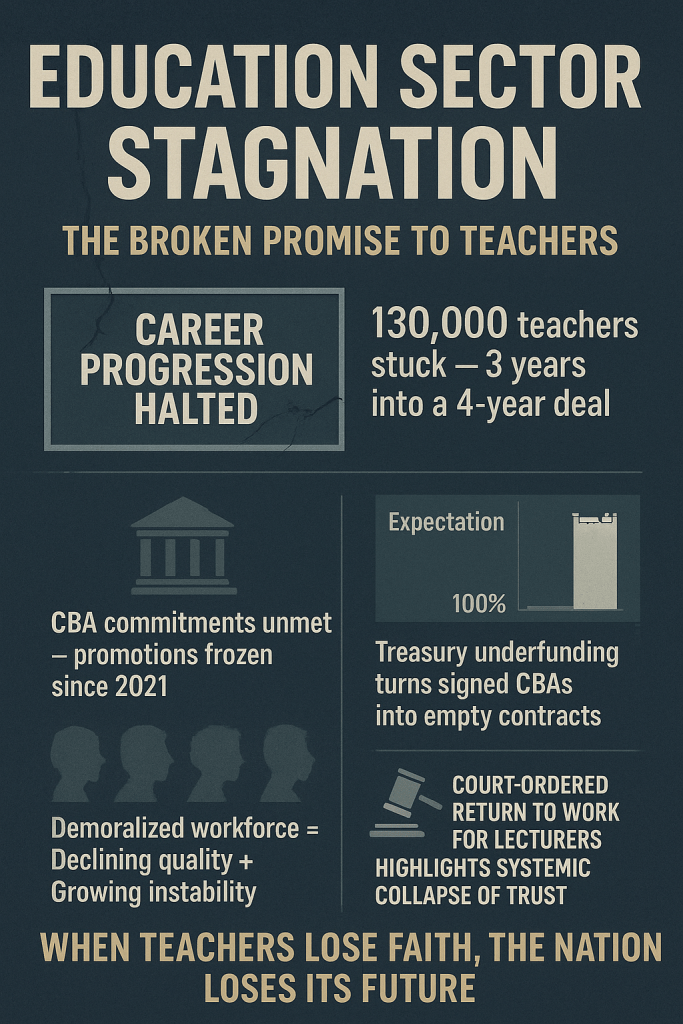
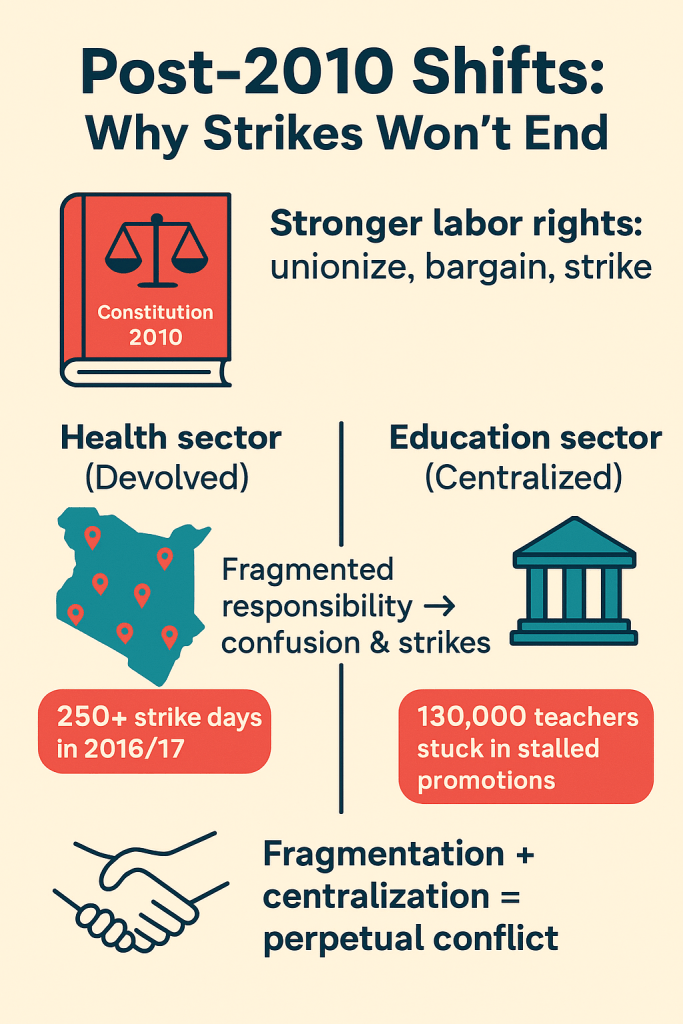
Kenya’s abrupt pivot to algorithmic oversight has exposed a wrenching trade-off: the same machines that can trace illicit flows also watch citizens’ everyday lives. As Safaricom’s AI began mapping transaction behaviors and regulators demanded real-time feeds, private data that once moved only between users and platforms is now visible to a new ecosystem of state and corporate watchers. That visibility matters: behavioural scoring, timing analysis, and API logs can unmask syndicates — but they can also profile law-abiding users, freeze livelihoods, or expose sensitive patterns (medical payments, political donations, remittance partners). In practice, this tension has a name and a face: legitimate attempts to close laundering loopholes (especially in betting and mobile lending) have collided with privacy norms codified under Kenya’s Data Protection laws and enforced by the Data Protection Commissioner. The friction is no longer theoretical — it plays out in court rulings and public grievances, where an automated alert can instantly strand a small-business owner awaiting payroll, or a migrant worker trying to send school fees home.
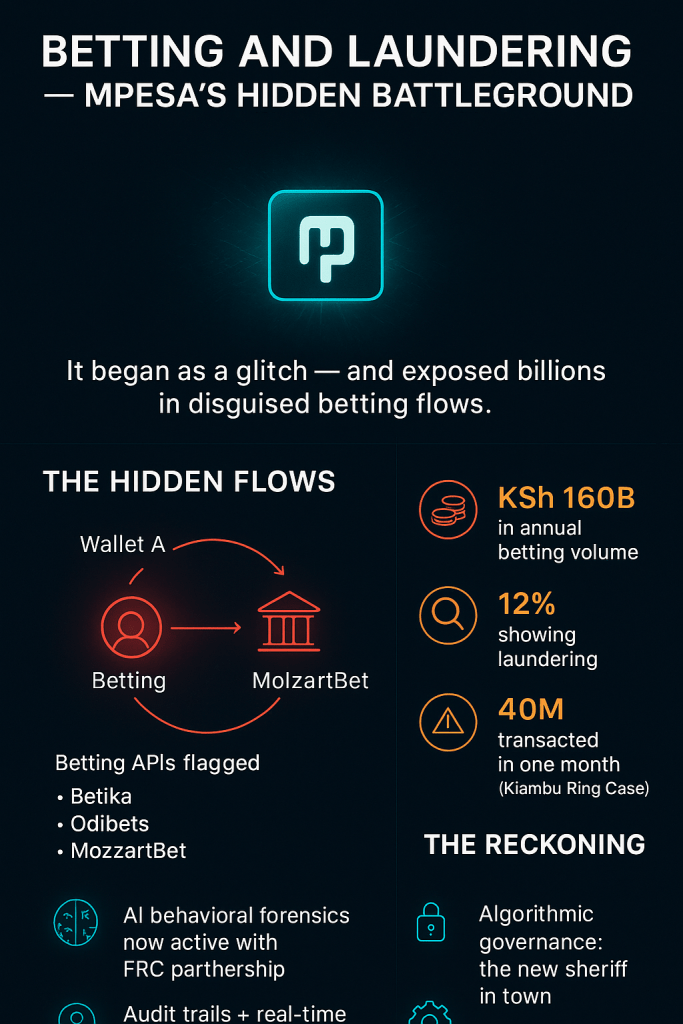
One high-profile example is the case involving Betika, which was ordered to pay KSh 250,000 for breaching data privacy rules. The ruling found that Betika had improperly processed users’ personal data without sufficient protections or lawful grounds. This case highlights a critical danger: when betting platforms (already under AML scrutiny) become nodes of state data demand, weak privacy compliance means corporate actors — not just regulators — can overreach data collection and usage, compounding surveillance risk. The Betika ruling proved that courts are willing to hold fintech operators accountable, but the scale of risk grows when those same APIs feed into AI-driven compliance systems without clear limits or safeguards.
The policy question is therefore blunt: how do you operationalize intrusive yet effective AML tools without creating a surveillance grid that punishes innocents? The answer requires more than slogans. It begins with strict, purpose-limited access: authorities and private partners should get only the minimal data needed to investigate a flagged flow — not full transaction histories. It requires explainable AI, where users receive understandable notices about why their wallet was flagged, and a clear appeals process exists. It demands robust oversight: the ODPC and FRC must enforce audit protocols, redress mechanisms, and limits on data retention and use. The Betika precedent is a warning: tightening oversight without privacy guardrails risks turning compliance into exclusion and exposing digital citizens to data abuse. Kenya now stands at a critical juncture: Will it build a system where enforcement respects rights — or drift into a regime where surveillance becomes default, and trust becomes collateral damage? In our next post, we’ll explore how to build explainable AI and regulatory harmony — practical steps to reconcile compliance, innovation, and rights.
References:
iGamingToday Betika ordered to pay KSh 250,000 for breaching data privacy rules
Subex How AI and Analytics Are Revolutionizing Fraud Detection in Mobile Money
Thomson Reuters AML challenges in evolving threat landscape, says ACAMS report
Techcabal How Safaricom’s AI exposed money laundering in Kenya’s betting boom