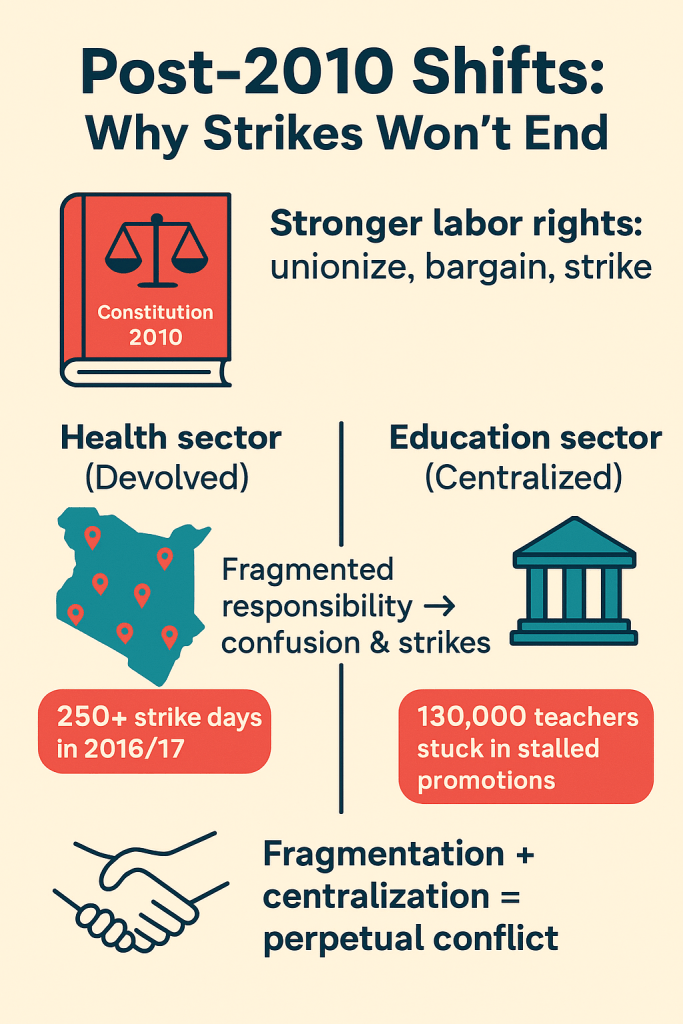
At the heart of Kenya’s endless labor unrest lies a contradiction the state has refused to confront: it preaches fiscal discipline while institutionalizing non-compliance. The Salaries and Remuneration Commission (SRC) — the body constitutionally mandated to manage public wage policy — has become a paradox of design: all authority, no enforcement. It issues guidelines that ministries and counties cite when cornered but ignore when expedient. Its circulars on pay harmonization and job evaluation are routinely undermined by politically negotiated allowances, ad hoc promotions, and extra-legal CBAs signed under pressure. The result is a regulatory void where fiscal control is performative and accountability optional. SRC’s power is largely symbolic — a watchdog muzzled by law and outpaced by politics — while the wage bill continues to balloon, not because of policy ignorance, but because institutions have learned how to outmaneuver oversight.
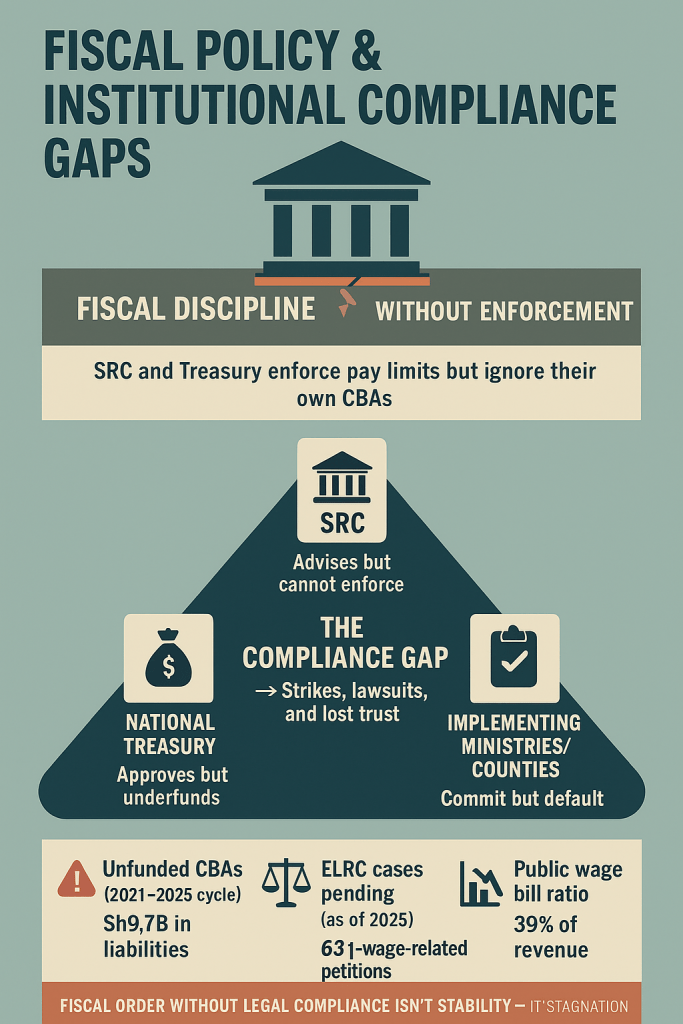
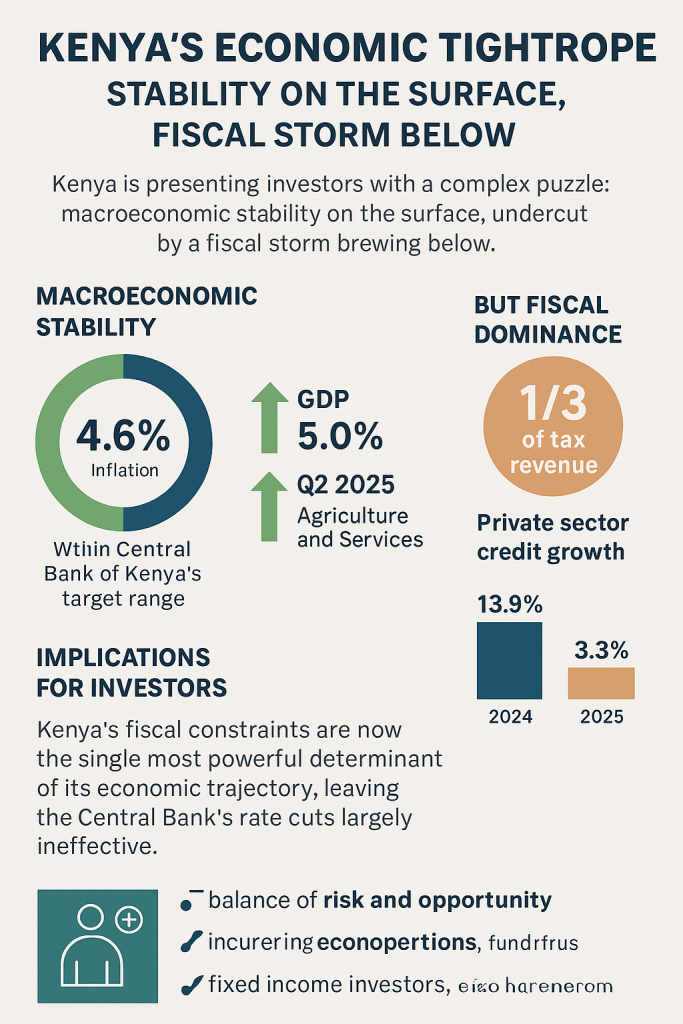
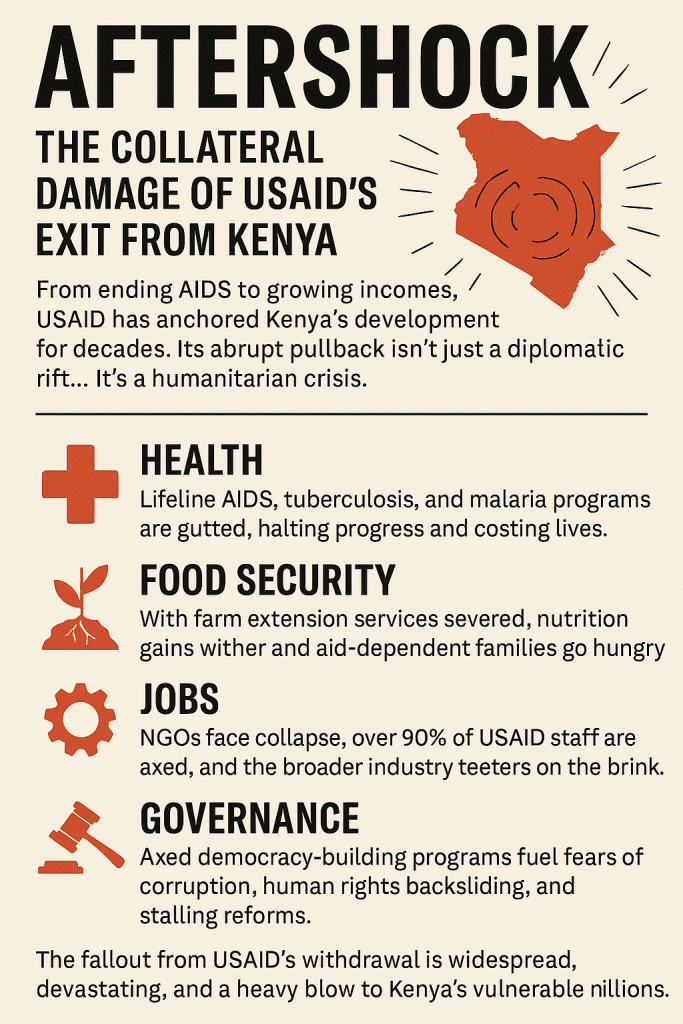
The National Treasury sits at the center of this dysfunction, weaponizing scarcity while mismanaging prioritization. Its annual insistence on fiscal prudence rings hollow against a record of delayed disbursements, unpaid CBA arrears, and selective funding of politically strategic programs. Treasury’s budgeting cycle has effectively become a tool of containment — a means to manage unrest rather than reform systems. When doctors, teachers, or civil servants strike, it is rarely due to wage greed; it is because their legally negotiated agreements remain unfunded despite formal approval. The Treasury’s pattern of signing off on CBAs without allocating corresponding funds has turned the entire labor framework into a credibility trap. Each unhonored agreement erodes faith not just in the fiscal system, but in the idea that government commitments are binding at all. This chronic underfunding blurs the line between austerity and abdication — and in doing so, transforms fiscal caution into a breeding ground for revolt.
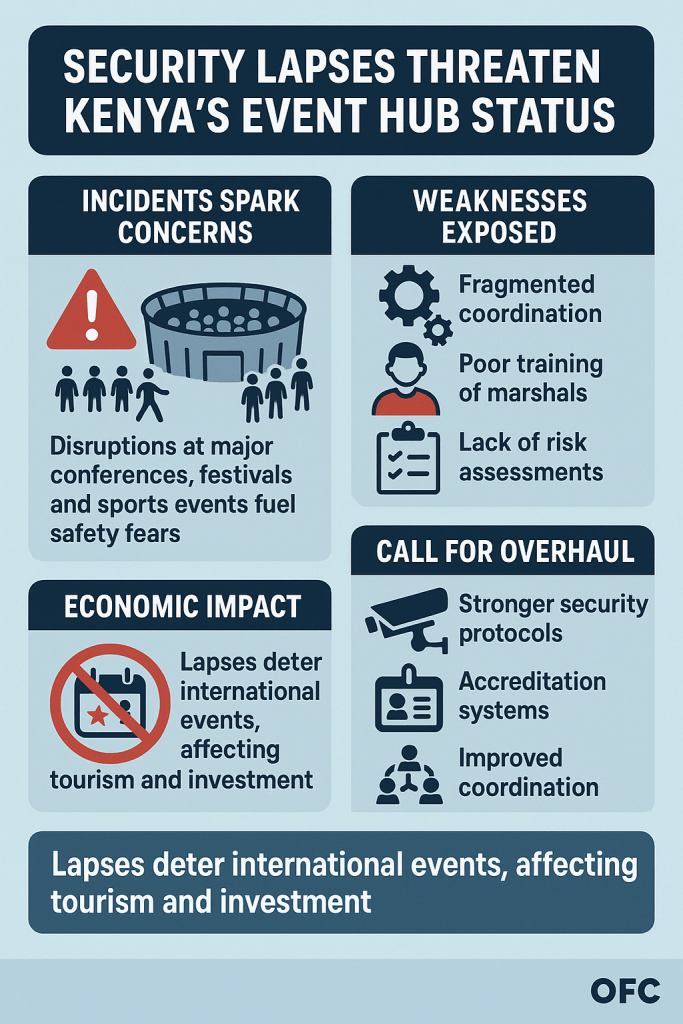
The compliance gap that emerges from this broken triangle — SRC, Treasury, and the implementing ministries or counties — is not administrative; it is existential. Each actor claims procedural innocence while collectively ensuring systemic failure. Ministries invoke budget ceilings; counties plead disbursement delays; SRC blames its limited mandate — and the Labor Ministry, the one body meant to arbitrate, has devolved into a crisis registrar. This institutional buck-passing is now a defining feature of Kenya’s governance culture. It explains why industrial action has become cyclical, why courts are perpetually mediating CBAs, and why public trust continues to collapse. Investors see it too: the volatility of Kenya’s labor market is not caused by worker militancy, but by the state’s refusal to honor its own laws. The strikes are symptoms — the disease is compliance failure dressed up as fiscal discipline. Until Kenya reforms the machinery of accountability between its fiscal and labor institutions, economic stability will remain an illusion built on broken promises.
References:
Daily Nation How bloated wage bills are choking counties and stalling development
Daily Nation A nation of protests and strikes
Business Daily Civil servants sue SRC over freezes on pay reviews