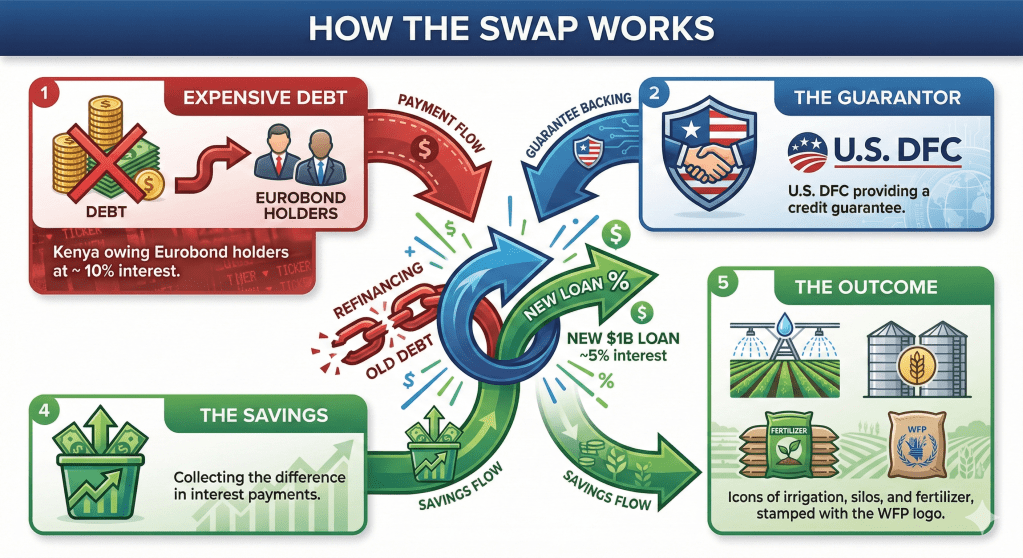
As the government targets 2 million acres for irrigation under the new debt swap initiative, the ghost of the Galana Kulalu project looms large. Just days ago, on January 26, 2026, the government announced plans for six new mega dams, signaling a return to the large-scale infrastructure strategy that failed so spectacularly in 2014. The original Galana Kulalu pilot consumed Sh7 billion to produce maize at costs higher than market price, collapsing under poor planning and corruption. Critics argue that repeating this “big dam” strategy ignores the hard-learned lessons of the past.
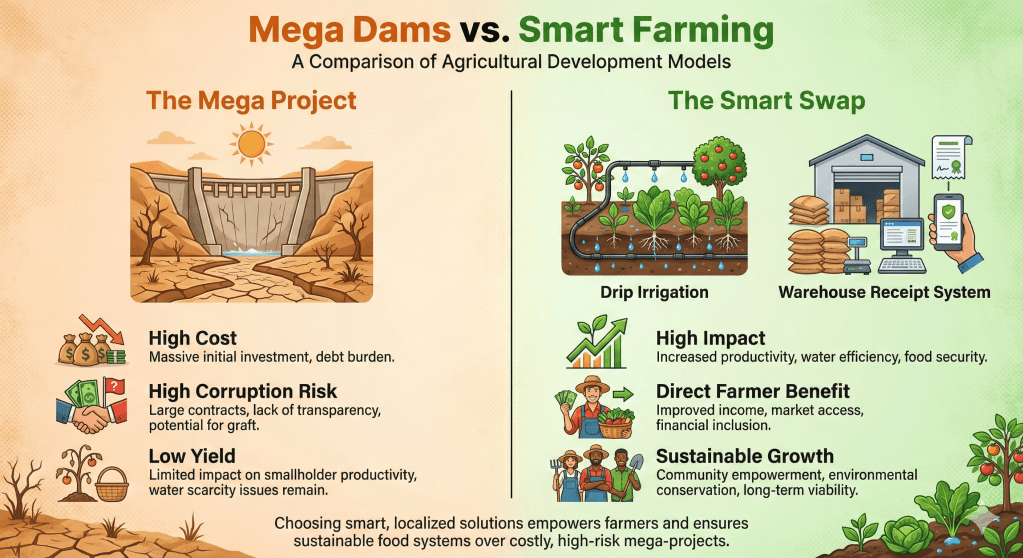
The disconnect is palpable. While the state plans mega-projects in arid lands, small-scale farmers—who produce the bulk of Kenya’s food—are struggling with basic input costs and lack of market access. The “savings” from the debt swap would likely yield higher returns if invested in decentralized solutions: household water pans, small-scale drip irrigation kits, and the Warehouse Receipt System (WRS) to help farmers store grain and avoid price exploitation by middlemen.
If the Sh129 billion is poured into another series of mega-dams, the funds risk being absorbed by contractors and consultants, leaving the country with more debt and no food. The success of this swap depends on shifting focus from concrete structures to the actual economics of farming—lowering production costs and ensuring profitability. Without this shift, we are merely “mixing oil and water” again, hoping that high-finance infrastructure will somehow trickle down to the grassroots.
References:
Capital Business Govt plans six mega dams, targets 2mn acres in irrigation push
The Star Government plans six mega dams, targets 2 million acres for irrigation push