Lake Nakuru, once Kenya’s unrivaled icon of flamingo tourism and a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is undergoing an environmental transformation that is quietly redefining its future. The dramatic shift from a shallow, alkaline soda lake to a swelling freshwater body—driven by climate change, deforestation, urban runoff, and persistent pollution—has reshaped not just the lake’s ecology, but also its economic and cultural purpose. Once celebrated as the “Lake of a Million Flamingos,” the site now faces a tourism identity crisis as its signature attraction—the vibrant flocks of Lesser Flamingos—has largely vanished due to the disappearance of Spirulina platensis, the algae they feed on. This ecological transition is not a fleeting anomaly; it signals a long-term reset, potentially stripping Kenya of one of its most iconic natural tourism assets.
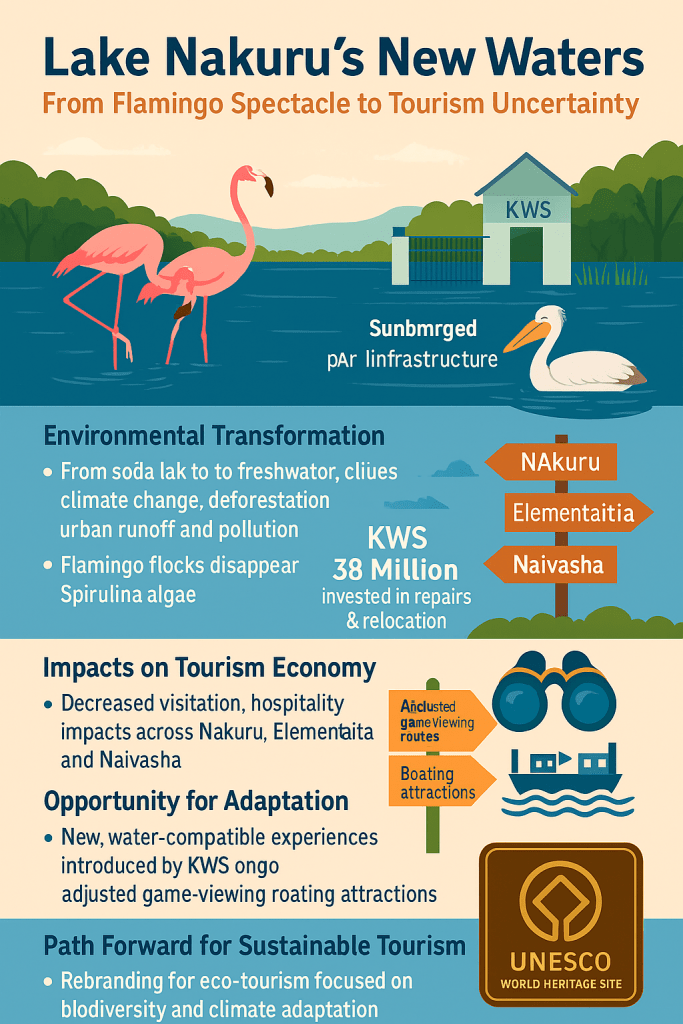
The implications for Kenya’s tourism economy are profound. Flamingo migration has dealt a blow to the local hospitality industry, with ripple effects felt from Nakuru to Elementaita and Naivasha. The park’s submerged infrastructure—gates, roads, and buildings—has necessitated a KSh 38 million investment in repairs and relocation, eating into Kenya Wildlife Service’s already stretched budget. Yet amid this disruption, opportunity glimmers. Kenya has a chance to reframe Lake Nakuru not as a site of lost heritage, but as a blueprint for adaptive, resilient tourism in the age of climate change. KWS has already introduced new water-compatible experiences, including adjusted game-viewing routes and potential boating attractions. With careful investment, storytelling, and conservation marketing, this shift can usher in a new kind of eco-tourism centered on freshwater biodiversity, migratory birds, and climate adaptation success stories.
But realizing this vision demands urgency, strategy, and inclusivity. Conservation and tourism authorities must actively engage displaced communities, whose turn to illegal fishing underscores a deeper social fragility tied to the lake’s changes. Tourism policy must evolve to support heritage resilience—protecting UNESCO designation through scientific reinterpretation of the site’s ecological value, not just nostalgia for what it once was. Lake Nakuru stands at the frontline of global climate impact on natural heritage. If Kenya can lead the world in repurposing this park’s brand while safeguarding its ecosystems and communities, it won’t just save a destination—it will create a model for climate-smart tourism across Africa and beyond.
References:
Scientific Research Assessment of Spatial Expansion of Rift Valley Lakes Using Satellite Data
The Standard State of three Rift Valley Lakes worry experts
Talk Africa Lake Nakuru’s Water levels Expected to Cause More Havoc During The Rainy Season, Experts Say
Jijuze Is Lake Nakuru’s Ecosystem at Risk Due to Pollution and Illegal Fishing?